1. What is the Circular Flow of income and what does it represent?
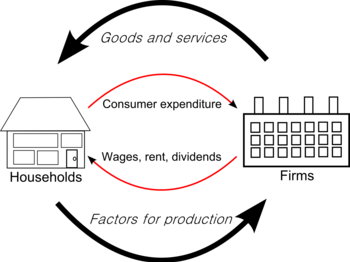
- The circular flow of income is representative of the economy, it shows the constant cycle of spending, output and income received by households and firms within an economy. It represents the relationship between Households and Consumers in terms of households gaining wages, in exchange firms gain consumers expenditure - The circular flow of income also indicates the withdrawals and injections into an economy.
- The diagram above illustrates the basic circular flow of income, Households are rewarded for the work input through wages, of that wage the disposable income is spent on goods and services provided by the firm - this results in the money returning to the firm in the form of revenue, and this cycle is repeated.
- An increase of injections into the economy is likely to have a positive multiplier effect. Increasing injections will result in more money in the economy, this would increase the size of the economy and encourage spending on consumer goods. A decrease of injections would have the opposite effect, it would cause consumers to save and result in the local economy improving as less imports are demanded.
- An increase in withdrawals will result in less money flowing within the economy, this could be through an increase in savings. An increase in taxes will result in a decrease in consumer spending, this will lower aggregate demand and result in less money within the circular flow.
- National Output is the value of the goods and services provided to households by firms, this is seen in the diagram as the curved arrow on top - this is the opposite of national expenditure which is the total amount spent on goods and services by a household. National income is the value of incomes received by households in exchange for capital, land and labor.
- The multiplier effect is the result of a change in economic policy that leads to a knock on effect within the economy. A multiplier effect can be both positive and negative - for example a decrease on income tax will result in an increase in consumer expenditure, this will result in an increase in revenues for firms, this has an beneficial impact on the economy. An example of a negative multiplier effect would be an increase in unemployment if tax's are increased.
- An increase in injections such as investment will result in better living standards for the general population, this is as a result of an increase of money with the circular flow of income that encourages firms to increase productivity as well as efficiency. For example investments to improve capital to encourage an increase in output will allow firms to decrease their average cost per unit and therefore supply it at a lower price into the market, this will encourage consumers to spend more as a result of the decrease in prices - this is returned to the firms in the form of revenues and the effect continues.
No comments:
Post a Comment